|
I'm a senior algorithm engineer at Farasis Energy. Prior on that, I received my PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Marquette University. I worked with Dr. Edwin Yaz in the Modeling, Analysis, Control and Estimation (MACE) Group at EECE Department, Marquette University. My research interest includes deep learning based computer vision, multi-object tracking, sensor network, sensor fusion, state estimation, parameter identification, distributed estimation theory and their applications. Computer vision & Deep Learning: I have 3 years academic experience in deep learning based image classification, object detection, video analysis, and milti-object tracking using state-of-the-art deep learning techniques. State & Parameter Estimation: I have over 8 years of research experience in state estimation, parameter identification and distributed estimation on sensor network using Kalman filter (and its variants like EKF, SPKF) based techniques. |

|
|
Just for fun, my Erdos Number is 5: Email / Resume / Google Scholar / Github / Linkedin / Research Gate / IEEE Xplore |
|
Jan/2026: Our paper "Online State of Health Estimaiton Using Approixmate Weighted Total Least Squares" will be available soon. Jan/2026: Our MECC 25 paper "Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Speed and Position Estimation Using Nonlinear Reduced-Order H-infinity Filter with Dynamic Uncertainties" is now available! Jun/2025: Our paper "Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Speed and Position Estimation Using Nonlinear Reduced-Order H-infinity Filter with Dynamic Uncertainties" is now accepted to MECC 2025, final version coming soon. Oct/2024: Our MECC 2024 paper is now available! Jul/2024: Our paper "Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Speed and Position Estimation Using Reduced-Order Extended Kalman Filter" is now accepted to MECC 2024, final version coming soon. Jun/2024: I defended my doctoral dissertation and received my doctorate degree! Jun/2024: Our paper "Multi-Object Tracking Using Video Sequences with Improved Performance and Reduced Computation Cost" is now accepted to CCTA 2024, final version coming soon. May/2024: Our paper "Reduced-order H-infinity Filter for Linear Systems" is now accepted to IECON 2024, final version coming soon. Dec/2022: Our CCTA 2022 paper is now available! Nov/2022: Our AVSS 2022 paper is now available! |
|
I'm interested in computer vision, especially using different deep learning methods to solve video based computer vision problems such as human behaviors recognition and object detection. I'm also working on distributed state and parameter estimation theory. In particular, I work on estimating State-of-Charge (SOC) and State-of-Health (SOH) of Lithium-ion cells using estimation theory. I'm also working on multi-target tracking problem in surveillance camera systems, which combines computer vision and distributed estimation problem together. |
|
|
|
Jiayi Su Project page coming soon A novel reduced-order non-linear filter for intermittent sensor measurement is developed for non-linear system state estimation |
|
|
Jiayi Su Project page coming soon A robust sensor fusion technique is developed for roll and pitch angle estimation using a 6-DoF IMU |
|
|
|
Jiayi Su project page Applying YOLOX to detect face masks in real time |
|
|
|
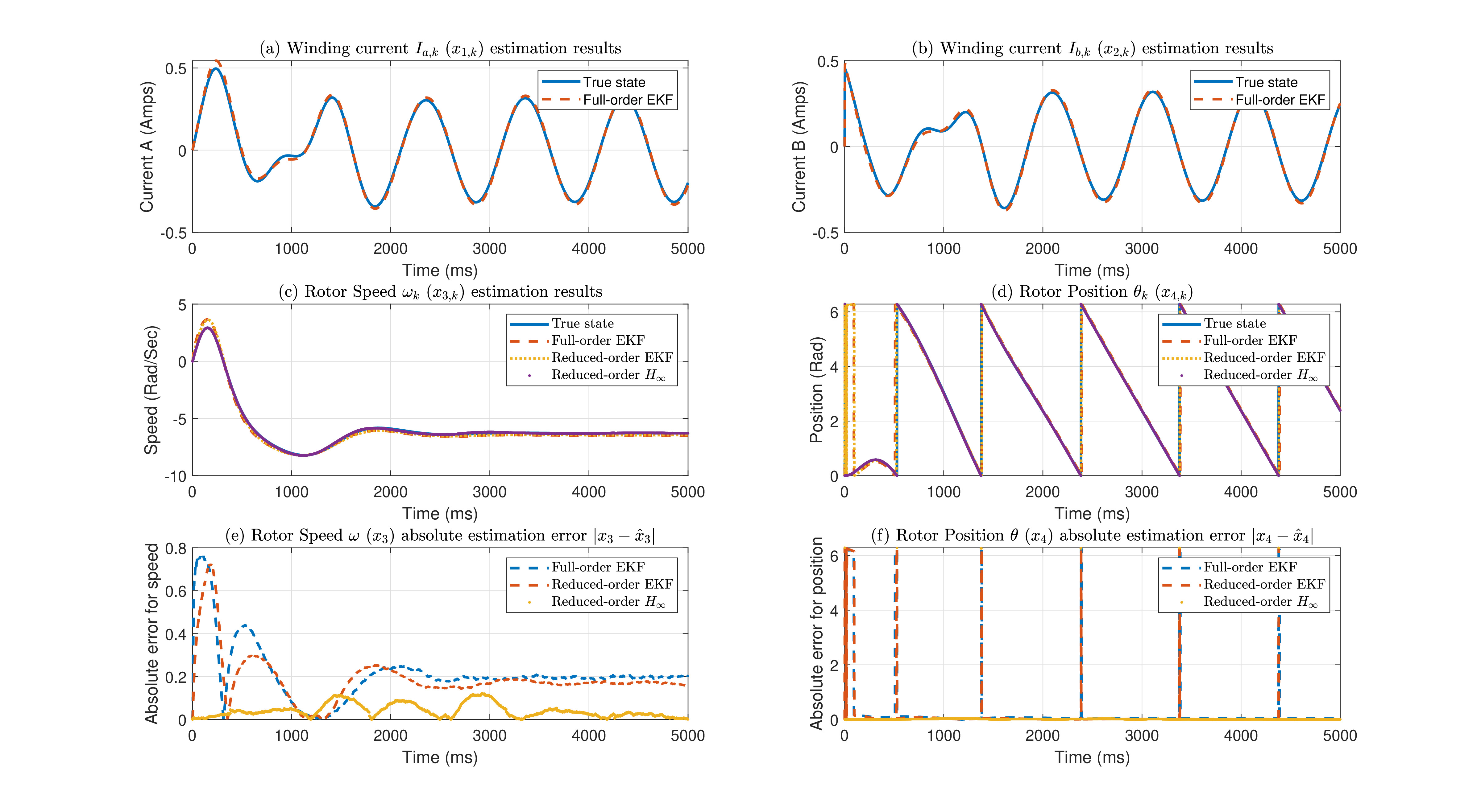
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Accepted to Modeling, Estimation and Control Conference(IFAC-PapersOnline-MECC), 2025 Abstract:Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) serves as a critical component in numerous industrial applications. Robust rotor speed and position estimates are essential for achieving precise motor control. Conventional approaches typically employ full-order nonlinear filters for state estimation. While since the winding currents are directly measurable, deploying a full-order observer to estimate all states becomes redundant. Furthermore, inherent system uncertainties - including modeling inaccuracies, temperature variations, and aging effects - can significantly compromise estimation accuracy. To address these challenges, a novel nonlinear reduced-order $H_{\infty}$ filter is introduced to estimate the speed and position of a two-phase PMSM with biased winding resistance. Simulation results show that the proposed filter brings robust estimation results compared to both full- and reduced-order EKFs if there exists model uncertainty. In addition, it can also be transformed to a reduced-order EKF for applications with accurate system dynamics as well. |
|
|
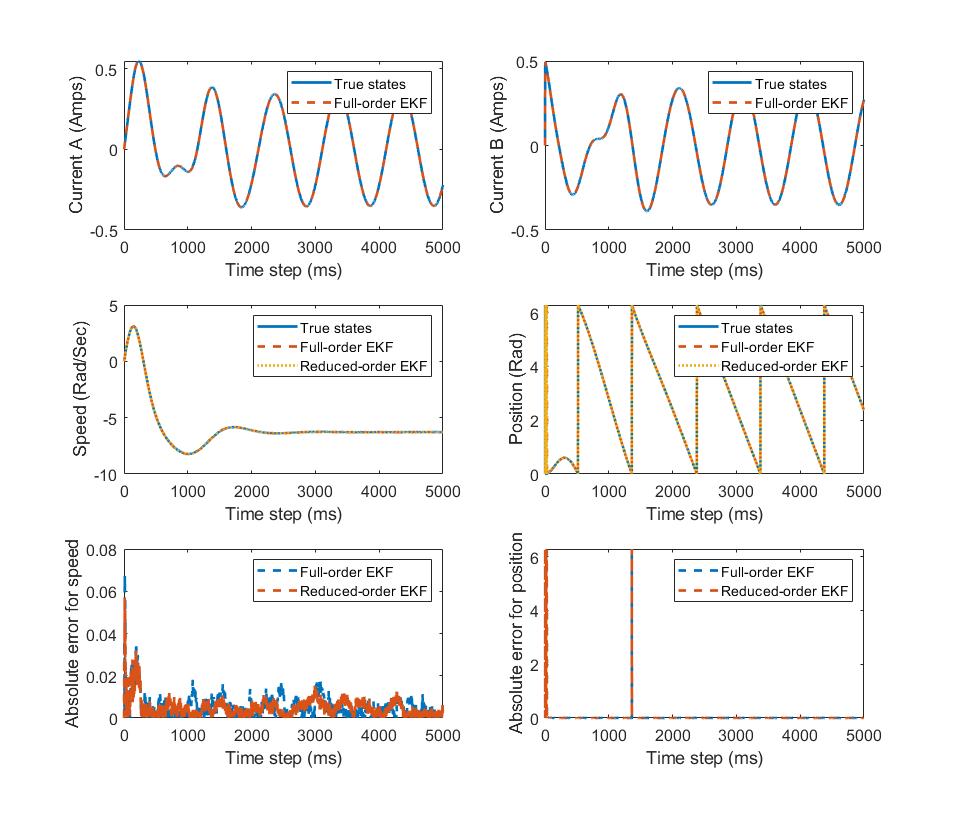
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Accepted to Modeling, Estimation and Control Conference(IFAC-PapersOnline-MECC), 2024 Abstract:Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) plays a pivotal role in many applications. Precise control of the PMSM necessitates accurate estimation of its states, particularly the motor's speed and position. Conventionally, a full-order Extended Kalman filter (EKF) is employed for state estimation. However, since the winding currents are directly measurable, deploying a full-order observer to estimate all states becomes unnecessary. In this work, a novel Reduced-order Extended Kalman filter (ROEKF) is introduced to estimate the speed and position of a two-phase PMSM. Simulation results show that the proposed ROEKF brings equivalent estimation accuracy compared to the full-order EKF, while it reduces the computation cost significantly. In addition, the proposed reduced-order filtering approach can be easily adapted to other applications to reduce the computation cost as well. |
|
|
|
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Accepted to Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), 2024 Abstract: Multi-object tracking (MOT) in video sequences is a fundamental problem in surveillance applications, aimed at robustly tracking multiple objects over time in video sequences. Following the tracking by detection framework, in this work, two efficient techniques are introduced to improve the tracking accuracy and reduce the computation complexity. Specifically, a more realistic motion model is used to improve the tracking performance with no extra computation cost, and a novel reduced-order Kalman filter is introduced to reduce the computation cost but with the same tracking accuracy compared to the full-order Kalman filter. Experimental results on MOT datasets show that the proposed method brings competitive results in terms of tracking accuracy and inference speed. In addition, the proposed techniques can easily be migrated into other trackers to improve their tracking performance. |
|
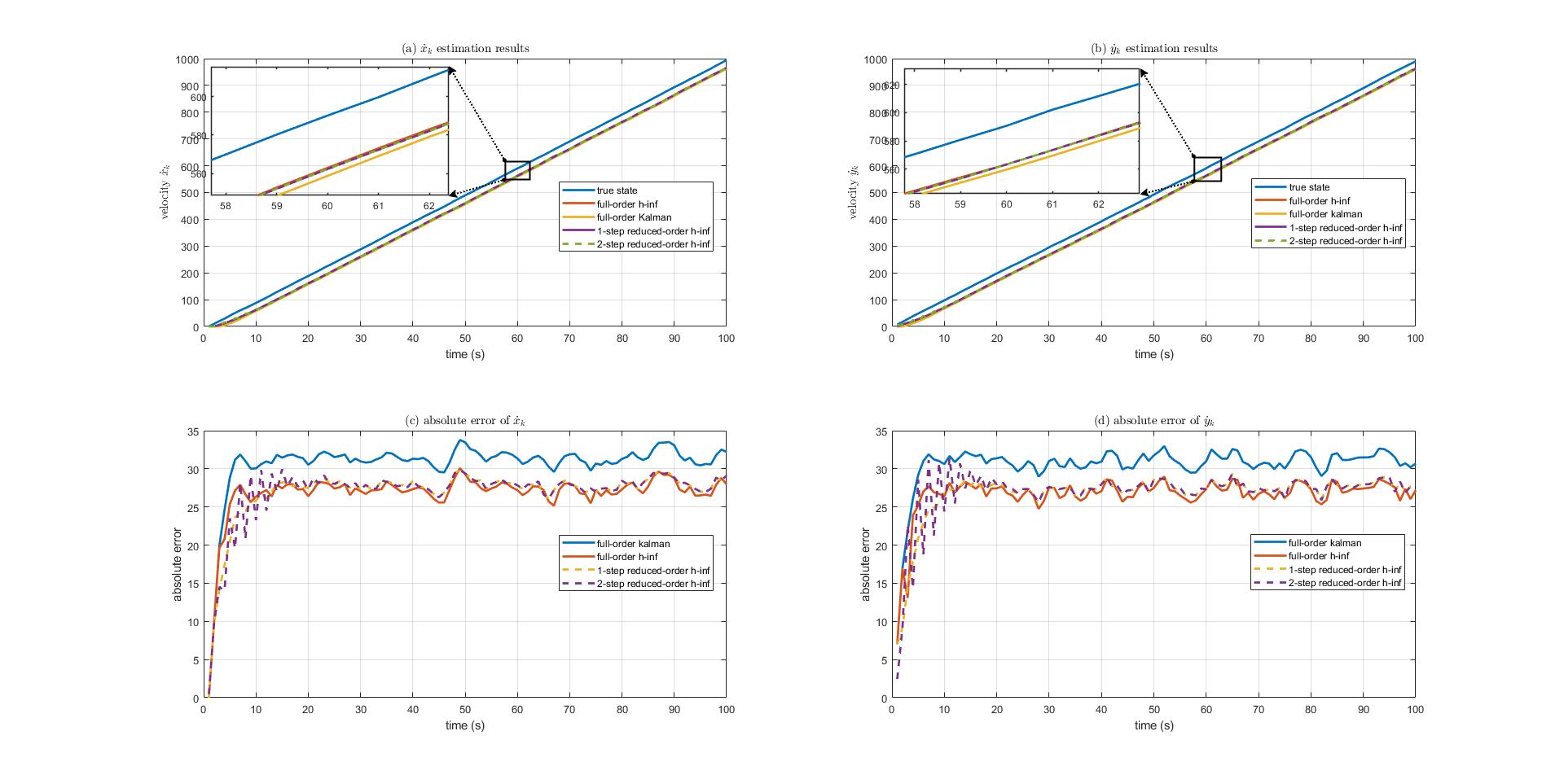
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Accepted to IEEE IECON 2024 Abstract: Robust state estimation plays a critical role in many applications, especially when system dynamics contain uncertainty, biased noise or perturbation. In this work, a novel discrete-time reduced-order H-infinity filter is introduced, where it offers a compelling alternative to the full-order H-infinity filter by significantly reducing computational costs without sacrificing its performance. Specifically, a novel 1-step, 2-step and steady-state reduced-order H-infinity filter are introduced. Simulations on a simple nearly constant velocity (NCV) model with biased process noise show that the proposed reduced-order H-infinity filters bring similar estimation accuracy compared to the full-order H-infinity filter under the same set up, while it reduces the computation cost significantly. In addition, the proposed reduced-order filtering approach can be easily adapted to other real-time applications to reduce the computation cost as well. |
|

|
Jiayi Su, Paris Her, Erik Clemens, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Henry Medeiros IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance (AVSS 2022) project page Abstract: Accurate detection of abnormal behavior can help improve public safety. In this work, a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) is implemented to detect violence captured by surveillance cameras. A comprehensive study of model hyper-parameter tuning is addressed to show competitive violence detection results using a general action recognition CNN without modifying the original architecture. Experimental results on three publicly available benchmark datasets show that the proposed method outperforms other sophisticated techniques designed specifically to detect violence in videos. Our analysis further indicates that reasonable network parameter adjustments can be an effective mechanism to guide the design of computer vision models in abnormal human behavior detection. |
|
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Fabien Josse Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), 2022 Abstract: Accurate State of Charge (SOC) and total capacity estimation are needed to ensure effective performance monitoring of Lithium-ion battery management systems. In this work, a Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE) technique is implemented to estimate SOC and cell total capacity simultaneously with an Enhanced Self-Correcting (ESC) model. In MMAE technique, conditional probabilities of all possible capacity values are computed to find the most probable cell capacity estimate, and SOC estimate is then calculated based on the given probabilities. Simulation results for a LiFePO4 Lithium-ion cell demonstrate that MMAE technique provides smaller estimation error compared to Joint and Dual estimation techniques. |
|
|
Jiayi Su, Alia Strandt, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Fabien Josse European Control Conference (ECC), 2021 Abstract: Lithium-ion battery cells are widely used in a variety of applications. An accurate online estimation technique to determine the State of Charge (SOC) can improve the safety of Lithium-ion cells, their performance and life cycle. However, nonlinear cell models bring many estimation challenges. In this work, an estimation technique which combines the Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE) and Extended Kalman filter (EKF) is introduced. The combination of these two techniques improves the SOC estimation accuracy and avoids each technique’s drawback. Simulation results for a LiFePO4 Lithium-ion cell demonstrate that this combined technique provides smaller estimation error compared to either MMAE or EKF alone. |
|
|
Jiayi Su, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Fabien Josse American Control Conference (ACC), 2021 Abstract: Accurate state of charge (SOC) estimation of Lithium-ion battery cells is critical since they are commonly used in a variety of applications. However, the complex chemical reactions inside the cell makes its model nonlinear, which increases the difficulty of the SOC estimation. An accurate online estimation technique to determine the SOC estimate can improve the safety of Lithium-ion cells. More importantly, cell performance and life cycle can also be improved. In this work, the nonlinear state estimation problem of determining SOC is converted to a linear estimation problem solved in a parallel fashion. Multiple model adaptive estimation (MMAE) technique based on a bank of Kalman filters is used to adaptively estimate the SOC. Simulation results for a LiFePO4 Lithium-ion battery cell demonstrate that this technique provides smaller estimation error compared to the Extended Kalman filter. |
|
|
Jiayi Su, Yuqin Weng, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC), 2020 Abstract: In this work, a new approach to detect sensor and actuator intrusion for Cyber-Physical Systems using a bank of Kalman filters is presented. The case where the unknown type of the intrusion signal is considered first, using two Kalman filters in a bank to provide the conditional state estimates, then the unknown type of intrusion signal can be detected properly via the adaptive estimation algorithm. The case where the target (either sensor or actuator) of the intrusion signal is unknown is also considered, using four Kalman filters in a bank designed to detect if the intrusion signal is about to affect healthy sensor or actuator signal. To test these methods, a DC motor speed control system subject to attack by different types of sensor and actuator signals is simulated. Simulations show that different types of sensor and actuator intrusion signals can be detected properly without the knowledge of the nature and the type of these signals. |
|
|
Jiayi Su, Yuqin Weng, Susan Schneider, Edwin Yaz, International Conference of Control, Dynamic Systems, and Robotics (CDSR), 2020 Abstract: Although Cyber-Physical Systems play a critical role in industrial production and our daily life, the safety of the CPS sensor and actuator signals have not been given due attention. In our previous work, a new approach which successfully detects CPS sensor and actuator intrusion using the multiple model estimation (MME) algorithm with a bank of Kalman filters was described. Since the earlier detection is of importance in such applications, in the present paper, an accelerated detection method using the fading memory technique is applied to the MME resulting in significant faster detection of intrusion signals. To verify the algorithm introduced in this paper, a DC motor speed control system subject to attack by different types of sensor and actuator signals is simulated. Simulations verify that the addition of the fading memory technique allows for the faster detection of sensor and actuator intrusions. |
|
Matrix Cookbook
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|